Is Physical security missing from your cybersecurity policy?

Physical security is an often forgotten or overlooked part of a corporate cybersecurity policy. To be effective a cybersecurity policy must be able to counter a cyberattack at any stage of what cyber experts call a cyber-kill chain.
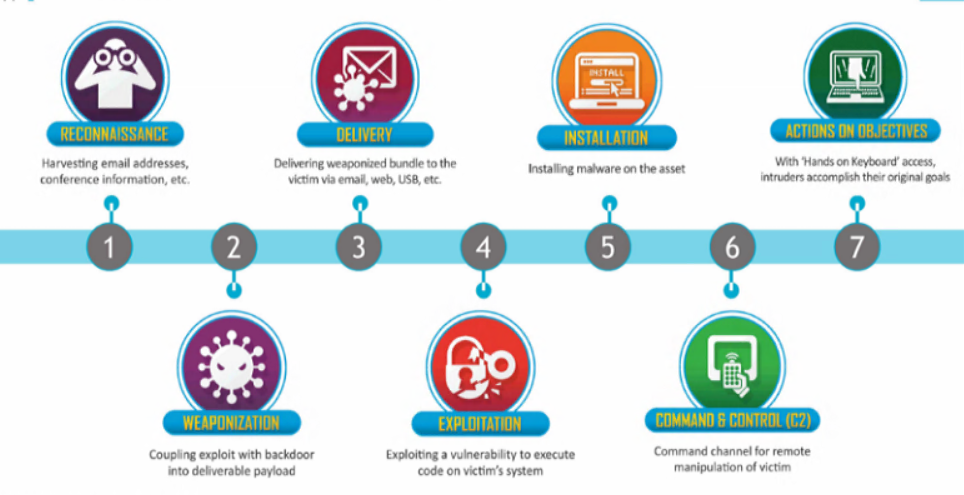
A cyberattack should follow a detailed and good plan. In general, hackers will follow a plan that consists of the following steps:
- Reconnaissance – passive and active
- Scanning
- Gain access
- Maintain access
- Cover tracks
The most important step in any cyberattack is the reconnaissance phase; the more information an attacker can gather on a target, the easier your task becomes. The term cybersecurity has become a confusing one in the industry over the last few years, and when people think about cybersecurity they probably assume it’s just limited to cyberspace. However, it is equally important to have a good physical security plan to complete this cybersecurity plan. This shared cyber and physical security is known as convergent security.
In this article, we provide information about different ways an attacker can use it in the real world to strengthen the reconnaissance performed online.
Physical security reconnaissance methods
Mapping out the targeted building
Often the targeted building is in a commercial or residential area, and an attacker can easily view the target without raising suspicion. This allows them to record positions of entry or exit points, such as windows and doors, determining whether employees need access cards and can duplicate them? Or maybe you’ll identify a warehouse door left open for delivery? They can see the life pattern of guards such as shift changes, the number of guards during the day and night, they can determine what the opening time of the building is and when it is busiest – if they decide to attack when they are calmer there is less chance of detection, if they attempt to access when it is busier they can mix with the crowd?
Telephotography
This is the act of taking pictures, using a telephoto lens. If a building has windows it can point to passwords, schedules, or any sensitive information written on a whiteboard or on the wall, for example.

Dumpster diving
This is where an attacker will search through the rubbish of an organization to find any sensitive information. This can include sensitive financial information, personal staff details, fixed head letters, etc. Information like this can be used in a variety of ways, such as spear phishing, bribery, intimidation, etc.

Shoulder surfing
Sometimes people decide to work away from the office, especially after the epidemic has shown that this can be just as productive as being at work. For example, a person can work in a coffee shop or on a train, and an attacker can position themselves in such a way that they can read the information on the screen. This can then be used in an online attack.

Electromagnetic intercept
A technique previously only available to state-sponsored actors, equipment can be used to intercept electromagnetic waves emitted from electronic devices. Equipment that can accurately analyze the keystrokes of a keyboard can be made from about $5000 and is effective against inexpensive USB keyboards, expensive wireless keyboards with signal encryption, and built-in notebook keyboards, Kaspersky reported.
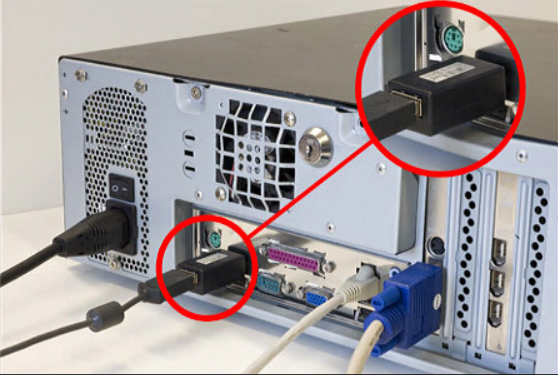
Physical access methods
Physical access can be used in both reconnaissance and gain access steps from an attack. If physical access is gained, an attacker can perform a more detailed mapping of the building, determine priority locations for future physical access, or be able to install equipment to assist in the access-gaining phase, such as installing keyloggers on computers to harvest user credentials, installing their hardware on network access points that can be used as vectors for cyberattack or upload malware from USB. If an attacker physically has access to a building, they can check tables, meeting rooms, closets, etc. for any sensitive information that could be used in an online attack.
Tailgating and social engineering
Tailgating is when an unauthorized person follows an employee after entering a building or room. Often an attacker can use social engineering in conjunction with such as holding heavy items so people keep the door open, dress in a typical work person’s uniform, or say they are there to fix something etc. In general, people trust and don’t like confrontation, which is why this type of violation is quite successful.

I hope you see how important it is to have a comprehensive and robust physical security plan as part of your cybersecurity plan. The attacker doesn’t need access to zero-day exploits, or the world famous APT to be successful for carrying out a cyberattack, if the attacker physically accesses your systems then the battle is lost before it starts.
