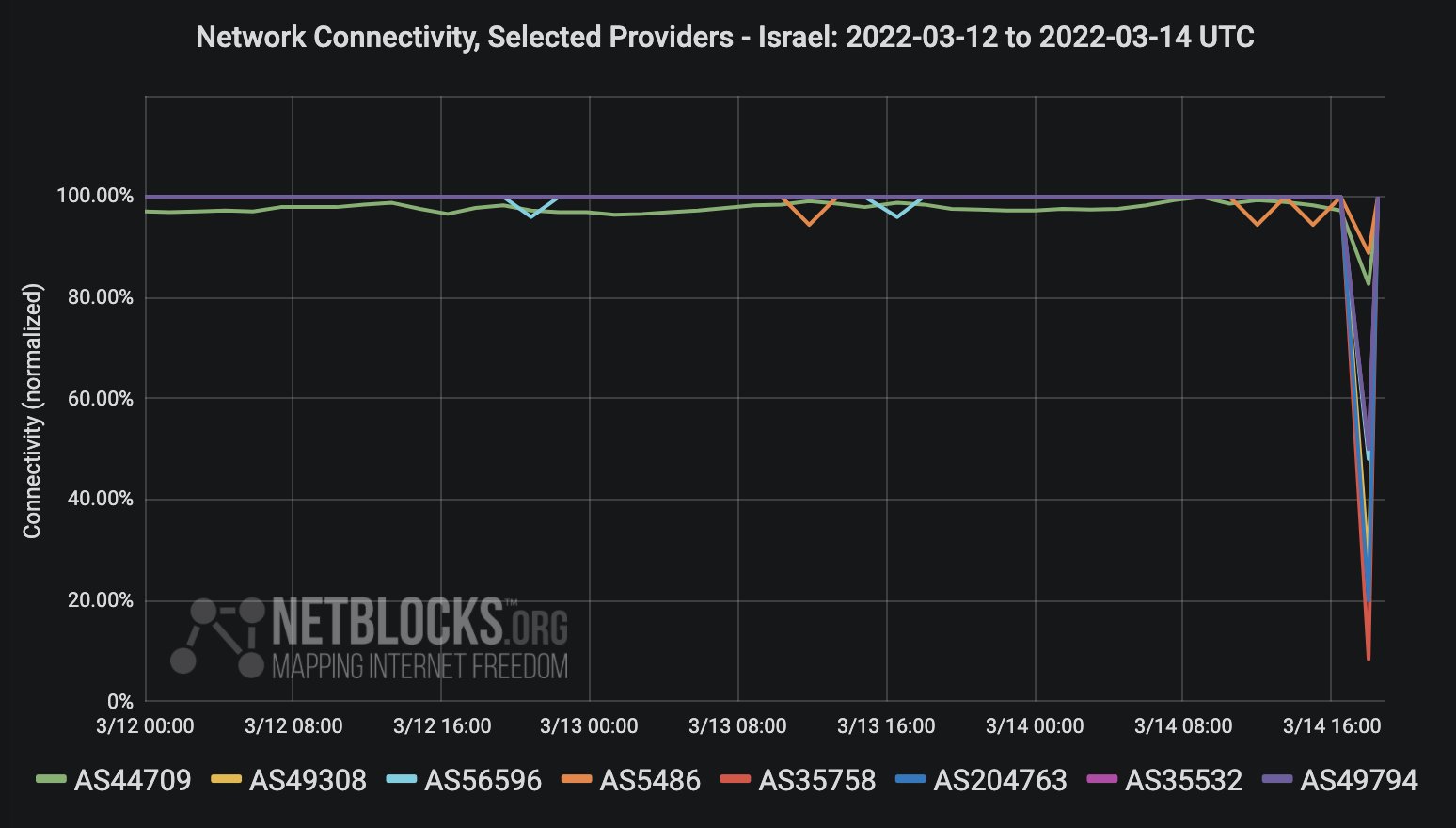
DDoS attack brings down Israeli government websites

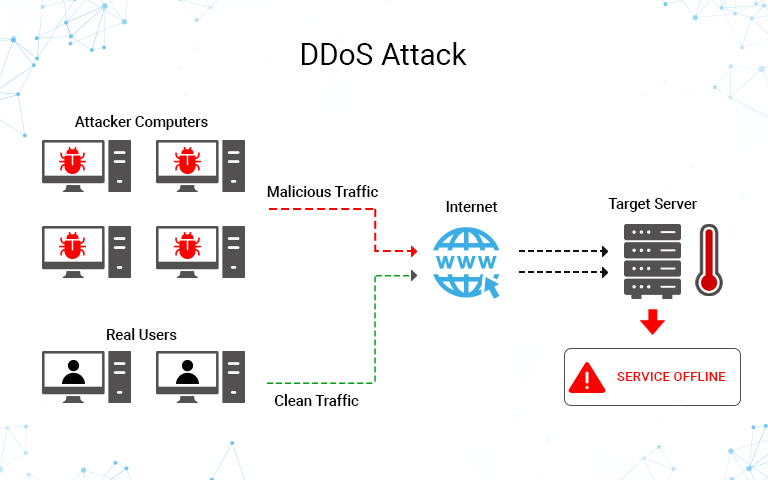
What is DDoS?
A short history of DDoS attack
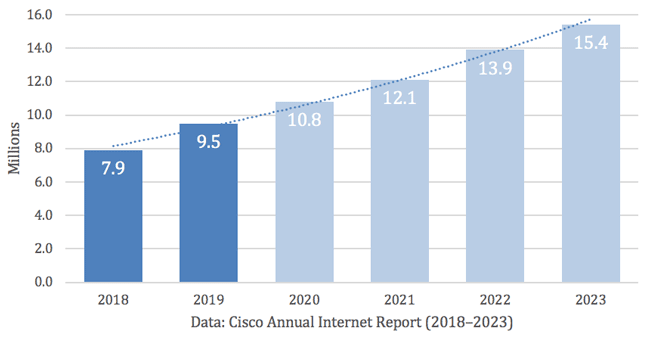
The first recorded DDoS attacks occurred in 1996 when an Internet service provider called Panixi was taken offline for several days by the SYN flood, a technique using TCP packages that has become a popular method of DDoS attack. Since then denial of service attacks has become one of the most commonly used tools for hackers to attack their victims, experts predict more than 15 million DDoS attacks will take place next year alone.
DDoS attacks are measured by the amount of data a botnet can send to its victim, one gigabit per second is enough to crash most organizations websites but modern attacks could be more than one terabit per second, the largest recorded attack so far was in 2021 against Russian company Yandek, which was bombarded with 22 million requests to its site per second
Famous DDoS attack
In October 2022 several Chinese ISPs attacked thousands of Google IP addresses lasting for six months and peaked at a whopping 2.5Tbps
In February 2022, Amazon Web Services was hit by a 2.3Tbps attack targeted at an unknown AWS client using a technique called the Connectionless Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (CLDAP), these techniques used a vulnerability to amplify the amount of data used in the attack by 70 times
In September 2016, cybersecurity expert Brain Krebs was attacked by a DDoS attack of more than 620 GIGABYTEs, the Krebs site had already been attacked, Krebs recorded 269 DDoS attacks since July 2012 but his attack was almost three times larger than anything the site or internet had seen before
October 2016 Dyn, a major domain name service (DNS) provider was attacked by a one terabit per second traffic flood that became the largest DDoS attack to date. the flood of traffic took down Dyns services rendering number of high profile websites such as GitHub, HBO, Twitter, Reddit, PayPal, Netflix and Airbnb inaccessible
Possible reason behind the attack
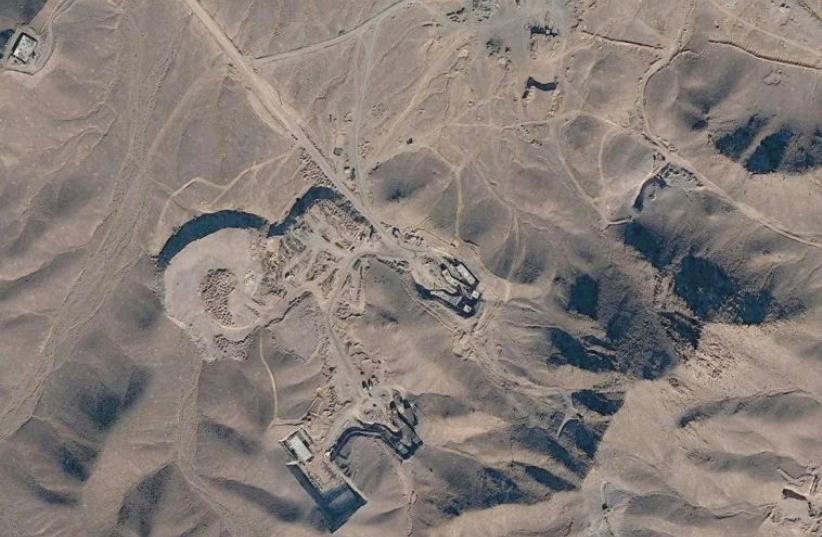

Fardow is the second largest site for enriching uranium after the Natanz facility, it is reported that Israeli intelligence and nuclear experts believe that is was previously intended to be where Iran would carry out the final stages of uranium enrichment to the 90% weaponized level as it is harder to attack from the air due to residing under a mountain .
Read The increasing problem of hacking in Iran to and the Hacker Series to find out more
